 BBC
BBCTechnology that identifies people at risk of heart attack in the next 10 years has been hailed as a “game changer” by scientists.
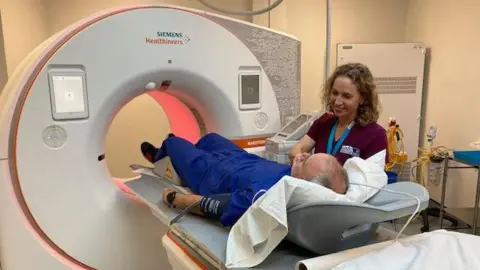
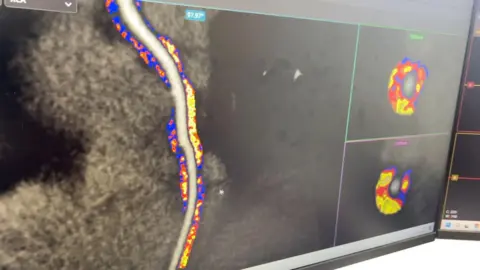
An artificial intelligence (AI) model detects heart inflammation that is not visible on CT scans, which involves a combination of X-rays and computer technology.
The pilot project, supported by NHS England, is running at five hospitals in Oxford, Milton Keynes, Leicester, Liverpool and Wolverhampton.
A decision on its use within the NHS is expected within months.
Its developer, an Oxford University spinout company, Caristo Diagnostics, says it is already working to adapt the technology to prevent stroke and diabetes.
“This technology is changing and the game is changing because for the first time we can see the natural processes that are invisible to the human eye, which lead to the development of narrowings and blockages. [within the heart],” said Professor Keith Channon, of Oxford University.
As part of the pilot, patients with chest pain referred for a CT scan are evaluated by Caristo Diagnostics’ CaRi-Heart AI platform.
The algorithm, which detects coronary inflammation and plaque, is then checked by trained staff to ensure accuracy.
Research has shown increased inflammation is associated with a greater risk of heart disease and fatal heart disease.
The British Heart Foundation (BHF) estimates that around 7.6 million people are living with heart disease in the UK and the annual cost to the NHS in England is £7.4bn, according to government figures.
Around 350,000 patients are sent for cardiac CT scans every year in the UK, the BHF said.
The Orfan Study (Oxford Risk Factors and Non-invasive imaging) involving 40,000 patients and published in Lancetfound that 80% of people were referred back to primary care without a defined prevention or treatment plan.
When they looked at that group, the researchers said they found that if patients had inflammation in their coronary arteries, they had a 20 to 30 times greater risk of having a heart attack. die of a heart attack in the next 10 years.
The study, supported by the BHF, found that by using AI technology, 45% of those patients were given medication or encouraged to make lifestyle changes to prevent the risk of a heart attack in the future.
‘Wake-up call’

Ian Pickford, 58, from Barwell in Leicestershire, was referred for a CT scan in November 2023, after experiencing persistent chest pains.
He was enrolled in the Orfan study at the University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust.
The double-glazed salesman has now been prescribed statins, told to quit smoking and increase his exercise after tests using an AI test showed he was at risk of heart disease.
Mr Pickford said: “It’s a big wake-up call.
“And when you see it on paper, you realize how serious it is. It’s something you can look at every day and think, ‘I’ve got to do something about this’.”
Professor Charalambos Antoniades, leader of the Orfan study, said the tools available so far are outdated because risk calculators can assess general risk factors, such as whether the patient has diabetes, smokes or fat.
He said: “Well, with this kind of [AI] technology, we know exactly which patient has disease activity in their veins before the disease develops.
“This means we can move early to stop the disease process and treat this patient to prevent the disease from developing and prevent heart disease from occurring.”
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence is evaluating the technology to determine whether it should be rolled out across the NHS.
It is being reviewed in the US and has been approved for use in Europe and Australia.
#Game #Changer #detects #hidden #risk #heart #disease #scientists
